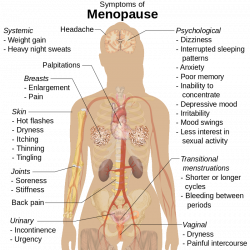
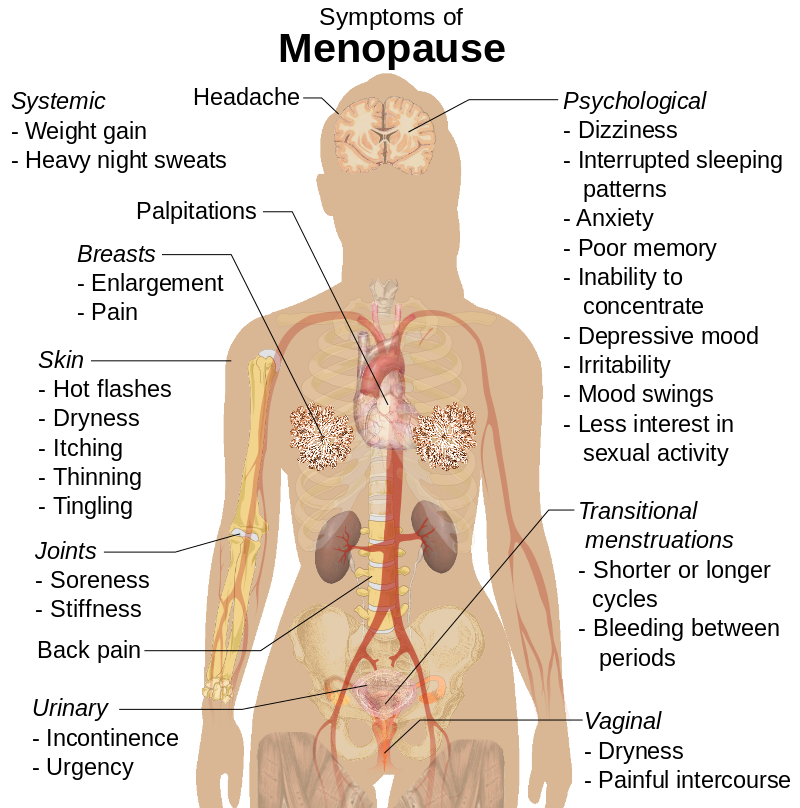
Menopause is the time in a woman's life when her normal menstrual periods stop and a woman's ovaries, the organs that produce eggs, stop producing female hormones. Menopause occurs at an average age of about 50, but the is usually 40–51 years of age, however it can occur earlier <40 years of age or be delayed (55 years or greater).
Two important hormones, oestradiol and progesterone, are made by the ovaries (the organs that produce eggs) in a cyclical fashion and help to maintain a normal menstrual cycle. When a woman reaches menopause, cyclical hormone production from the ovaries stops, leading to a cessation in monthly menstrual periods and of egg production.
The menopausal change is slow and usually takes two to five years to complete. During this so-called peri-menopausal phase (also sometimes referred to as ‘the climacteric’ or ‘the change’), hormone levels can fluctuate from high to low and from one month to the next. Some months a woman may have a period but then go for several months without a period. It is important to note that during this time, a woman may still be able to get pregnant. Menopause is said to have taken place when a woman has not had a period for 12 months. Menopause happens naturally as a woman ages. However, menopause can also occur for other reasons, including the removal of the ovaries for cancer or other medical reasons like endometriosis.