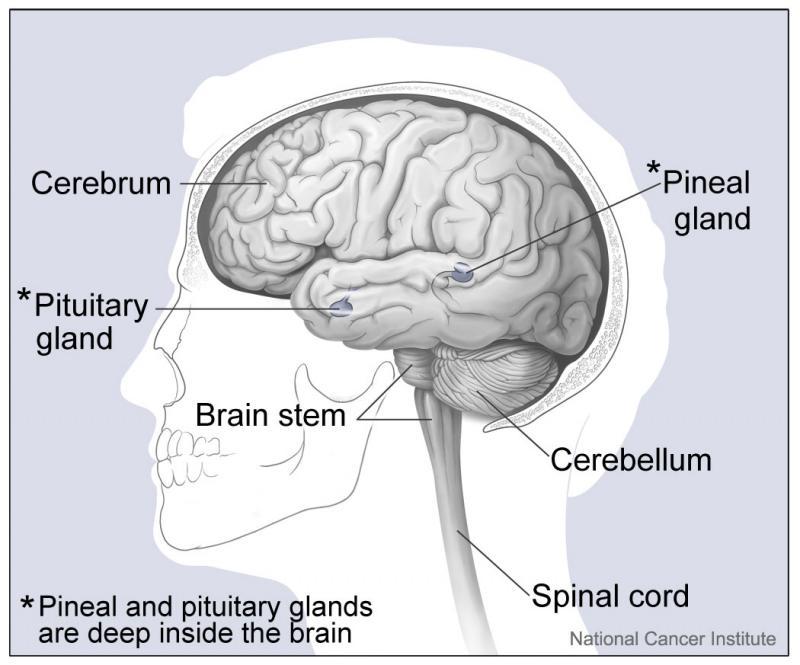
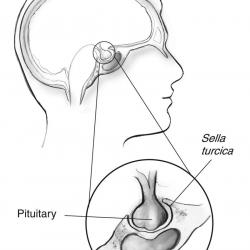
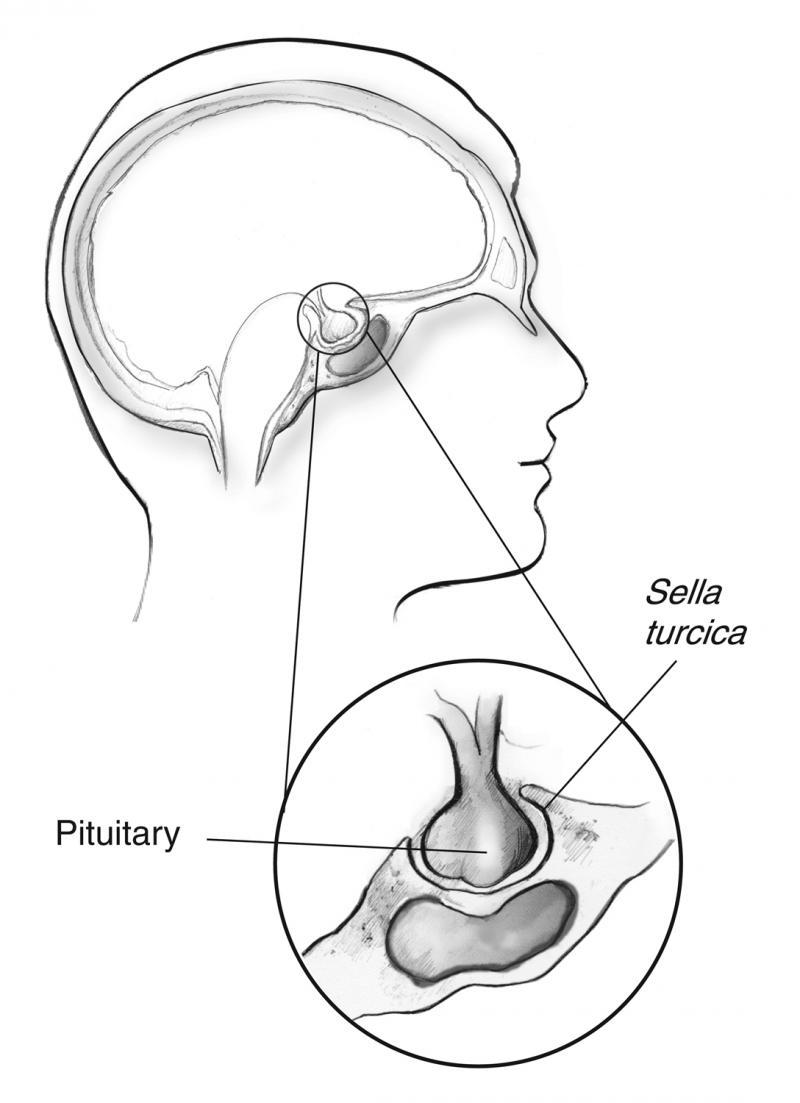
The pituitary is a pea-sized gland that is attached to an area at the base of the brain called the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland is part of the endocrine system; a system of glands that produce and regulate hormones. The hypothalamus communicates with the rest of the brain and nervous system. It senses the body’s need for more or less of a particular hormone and controls the amount of hormone released from the pituitary. Pituitary disorders are characterised by an excess or a deficiency in one or more of the hormones produced by the pituitary gland. When the disorder is caused by a pituitary tumour, symptoms such as headache and loss of vision may be present due to compression of the surrounding tissues.
The pituitary consists of a front (anterior) and back (posterior) portion. In the anterior pituitary, growth hormone (GH), adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), luteinising hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and prolactin are produced. They affect particular “target” tissues throughout the body, including the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, ovaries (women), and testes (men). Oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) are produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary for release. Some of the normal functions of these hormones are described below.
- GH: Regulates bone growth and muscle mass.
- ACTH: Regulates the body’s response to stress by stimulating cortisol production by the adrenal glands.
- TSH: Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones, which regulate the rate at which the body uses energy (the metabolic rate).
- LH and FSH: Required for the development of sexual characteristics at puberty and fertility.
- Prolactin: Stimulates breast milk production after childbirth.
- ADH: Controls the amount of water that the kidneys excrete, which in turn helps regulate the balance of water in the body.
- Oxytocin: Stimulates the contraction of the uterus during and after childbirth and is responsible for stimulating the release of milk during breastfeeding.